 Programs
tab
Programs
tab  Programs
tab
Programs
tab
|
Click the numbers to learn about specific controls, or read an introduction.
|
Use this tab to:
|
A green check means the program is allowed access/server rights. |
|
|
A red X means the program is denied access/server rights. |
|
|
A blue question mark means ZoneAlarm Pro will display a Program alert when the program asks for access/server rights. |
![]() Note:
By default, programs to which you give access or server permission can use all
ports. For additional security, use the Ports
tab to limit the ports a program can use.
Note:
By default, programs to which you give access or server permission can use all
ports. For additional security, use the Ports
tab to limit the ports a program can use.
![]() Tip You
can sort the programs in the list by any field. Click on the field header to
sort. The arrow icon
Tip You
can sort the programs in the list by any field. Click on the field header to
sort. The arrow icon ![]() indicates the sort order.
indicates the sort order.
As you use your computer, ZoneAlarm Pro detects every program that requests network access and adds it to this list. It also records the answer you gave to the Program alert for that program. A green bullet in the Active column means the program listed is currently accessing network resources. The program column displays the program name and associated icon.
![]() Tip
For more information about a program, click the program name, then look in the
Entry Details box at the bottom of the screen.
Tip
For more information about a program, click the program name, then look in the
Entry Details box at the bottom of the screen.
Use these fields to establish access permission and server permission for a program.
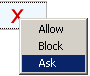
To change a permission setting, click the symbol, then select from the shortcut menu. |
|
|
|
Menu item |
Description |
|
Changes Frequently |
If this option is selected, ZoneAlarm Pro will use only file path information only to authenticate the program. The MD5 signature will not be checked.
|
|
Options |
Opens the Program Options dialog box, in which you can customize port permissions and security options for the program. |
|
Properties |
Opens your operating system's properties dialog box for the program. |
|
Remove |
Deletes the program from the list. |
|
Add program |
Opens an explorer window so you can browse to a program on your computer that you want to add to the list. |
![]() Note
Built-in rules ensure a consistent security policy for each program. Programs
with access to the Internet Zone also have access to the Trusted Zone, and programs
with server permission in a Zone also have access permission for that Zone.
This is why (for example) selecting Allow under Trusted Zone/Server automatically
sets all of the program's other permissions to Allow.
Note
Built-in rules ensure a consistent security policy for each program. Programs
with access to the Internet Zone also have access to the Trusted Zone, and programs
with server permission in a Zone also have access permission for that Zone.
This is why (for example) selecting Allow under Trusted Zone/Server automatically
sets all of the program's other permissions to Allow.
A key symbol in this field indicates that the program has pass-lock privilege.
To give pass lock privilege to a program, click the lock column, then choose Pass-Lock from the shortcut menu.
To revoke pass-lock privilege, click the lock icon, then choose Normal from the shortcut menu.
![]() Tip
If you grant pass-lock permission to a program, and that program uses other
applications to perform its functions (for example, services.exe), be sure to
give those other programs pass-lock permission as well.
Tip
If you grant pass-lock permission to a program, and that program uses other
applications to perform its functions (for example, services.exe), be sure to
give those other programs pass-lock permission as well.
The entry detail box displays information about the program currently selected in the programs list.
|
Field |
Information |
|
Product name |
The common name of the program, for example, Internet Explorer. |
|
File name |
The fully-qualified name of the executable file, for example, C:\\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEXPLORE.EXE |
|
Version |
The version number of the program. |
|
Created date |
The date the program was created by its manufacturer. |
|
File size |
The size of the executable file |
Use these buttons to add a program to the programs list, or to access program options for the currently selected program.
Click Add to add a program to the programs list.
Click Options to access the Ports tab and Security tab in the Program Options dialog box.
For more information about the Program Options dialog, see the related topics, Ports tab and Security tab.
Program control
Privacy protection
Ports tab
Security tab
pass-lock
When the Internet Lock is engaged, programs given pass-lock permission can continue
accessing the Internet. Access permission and server permission for all other
programs is revoked until the lock is opened.
access permission
Access permission allows a program on your computer to initiate communications
with another computer. This is distinct from server permission, which allows
a program to "listen" for connection requests from other computers.
You can give a program access permission for the Trusted Zone, the Internet
Zone, or both.
Several common applications may need access permission to operate normally. For example, your browser needs access permission in order to contact your ISP's servers. Your e-mail client (for example, MS Outlook) needs access permission in order to send or receive e-mail.
The following basic options are available for each program:
Allow
the program to connect to computers in the Internet Zone / Trusted Zone
Block the program from accessing computers in the Internet Zone / Trusted
Zone
Ask whether the program should have access permission (show Repeat
Program alert)
server permission
Server permission allows a program on your computer to "listen" for
connection requests from other computers, in effect giving those computers the
power to initiate communications with yours. This is distinct from access permission,
which allows a program to initiate a communications session with another computer.
Several common types of applications, such as chat programs, e-mail clients, and Internet Call Waiting programs, may need server permission to operate properly. Grant server permission only to programs you're sure you trust, and that require it in order to work.
If possible, avoid granting a program server permission for the Internet Zone. If you need to accept incoming connections from only a small number of machines, add those machines to the Trusted Zone, and then allow the program server permission for the Trusted Zone only.
The following basic options are available for each program
Allow
the program to listen for connection requests
Block the program from listening for connection requests
Ask me whether to allow the program to listen for connection requests
(show Server Program alert)